MatplotlibChart
Bases: Container
Displays a Matplotlib chart.
Warning
This control requires the matplotlib
Python package to be installed.
See this installation guide for more information.
adaptive: bool | None = None
adaptive property can be specified for a control in the following cases:
- A control has matching Cupertino control with similar functionality/presentation
and graphics as expected on iOS/macOS. In this case, if
adaptiveisTrue, either Material or Cupertino control will be created depending on the target platform.
These controls have their Cupertino analogs and adaptive property:
* AlertDialog
* AppBar
* Checkbox
* ListTile
* NavigationBar
* Radio
* Slider
* Switch
- A control has child controls. In this case
adaptiveproperty value is passed on to its children that don't have theiradaptiveproperty set.
The following container controls have adaptive property:
* Card
* Column
* Container
* Dismissible
* ExpansionPanel
* FletApp
* GestureDetector
* GridView
* ListView
* Page
* Row
* SafeArea
* Stack
* Tabs
* View
alignment: Alignment | None = None
Align the child control within the container.
Value is of type Alignment.
animate: AnimationValue | None = None
Enables container "implicit" animation that gradually changes its values over a period of time.
Value is of type AnimationValue.
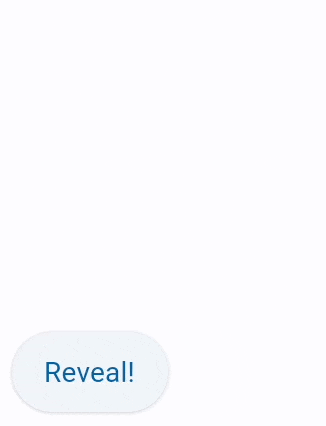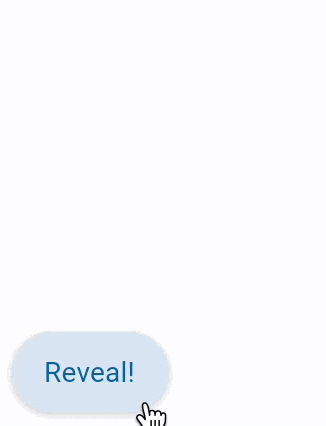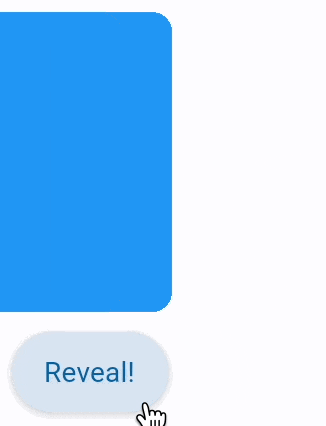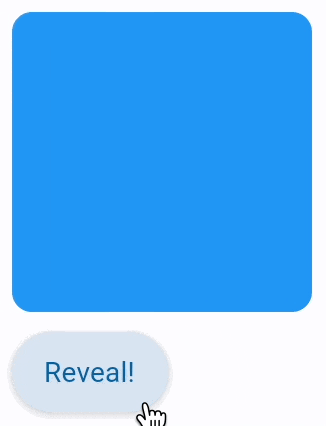
animate_offset: AnimationValue | None = None
Setting control's animate_offset to either True, number or an instance of
animation.Animation class enables implicit animation of Control.offset property.
offset property is an instance of transform.Offset class which specifies
horizontal x and vertical y offset of a control scaled to control's size.
For example, an offset transform.Offset(-0.25, 0) will result in a horizontal
translation of one quarter the width of the control.
Offset animation is used for various sliding effects:
import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
c = ft.Container(
width=150,
height=150,
bgcolor="blue",
border_radius=10,
offset=ft.transform.Offset(-2, 0),
animate_offset=ft.animation.Animation(1000),
)
def animate(e):
c.offset = ft.transform.Offset(0, 0)
c.update()
page.add(
c,
ft.ElevatedButton("Reveal!", on_click=animate),
)
ft.run(main)
animate_opacity: AnimationValue | None = None
Setting control's animate_opacity to either True, number or an instance of
animation.Animation class enables implicit animation of Control.opacity
property.
import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
c = ft.Container(
width=150,
height=150,
bgcolor="blue",
border_radius=10,
animate_opacity=300,
)
def animate_opacity(e):
c.opacity = 0 if c.opacity == 1 else 1
c.update()
page.add(
c,
ft.ElevatedButton(
"Animate opacity",
on_click=animate_opacity,
),
)
ft.app(main)
animate_position: AnimationValue | None = None
Setting control's animate_position to either True, number or an instance of
animation.Animation class (see above) enables implicit animation of Control's
left, top, right and bottom properties.
Please note Control position works inside Stack control only.

import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
c1 = ft.Container(width=50, height=50, bgcolor="red", animate_position=1000)
c2 = ft.Container(
width=50, height=50, bgcolor="green", top=60, left=0, animate_position=500
)
c3 = ft.Container(
width=50, height=50, bgcolor="blue", top=120, left=0, animate_position=1000
)
def animate_container(e):
c1.top = 20
c1.left = 200
c2.top = 100
c2.left = 40
c3.top = 180
c3.left = 100
page.update()
page.add(
ft.Stack([c1, c2, c3], height=250),
ft.ElevatedButton("Animate!", on_click=animate_container),
)
ft.run(main)
animate_rotation: AnimationValue | None = None
Setting control's animate_rotation to either True, number or an instance of
animation.Animation class enables implicit animation of Control.rotate
property.
from math import pi
import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
c = ft.Container(
width=100,
height=70,
bgcolor="blue",
border_radius=5,
rotate=ft.transform.Rotate(0, alignment=ft.Alignment.CENTER),
animate_rotation=ft.animation.Animation(300, ft.AnimationCurve.BOUNCE_OUT),
)
def animate(e):
c.rotate.angle += pi / 2
page.update()
page.vertical_alignment = ft.MainAxisAlignment.CENTER
page.horizontal_alignment = ft.CrossAxisAlignment.CENTER
page.spacing = 30
page.add(
c,
ft.ElevatedButton("Animate!", on_click=animate),
)
ft.run(main)
animate_scale: AnimationValue | None = None
Setting control's animate_scale to either True, number or an instance of
animation.Animation class enables implicit animation of Control.scale
property.
import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
c = ft.Container(
width=100,
height=100,
bgcolor="blue",
border_radius=5,
scale=ft.transform.Scale(scale=1),
animate_scale=ft.animation.Animation(600, ft.AnimationCurve.BOUNCE_OUT),
)
def animate(e):
c.scale = 2
page.update()
page.vertical_alignment = ft.MainAxisAlignment.CENTER
page.horizontal_alignment = ft.CrossAxisAlignment.CENTER
page.spacing = 30
page.add(
c,
ft.ElevatedButton("Animate!", on_click=animate),
)
ft.run(main)
blend_mode: BlendMode | None = None
The blend mode applied to the color or gradient background of the container.
Value is of type BlendMode and
defaults to BlendMode.MODULATE.
blur: BlurValue | None = None
Applies Gaussian blur effect under the container.
The value of this property could be one of the following:
- a number - specifies the same value for horizontal and vertical sigmas, e.g.
10. - a tuple - specifies separate values for horizontal and vertical sigmas, e.g.
(10, 1). - an instance of
Blur
For example:
ft.Stack(
[
ft.Container(
content=ft.Text("Hello"),
image_src="https://picsum.photos/100/100",
width=100,
height=100,
),
ft.Container(
width=50,
height=50,
blur=10,
bgcolor="#44CCCC00",
),
ft.Container(
width=50,
height=50,
left=10,
top=60,
blur=(0, 10),
),
ft.Container(
top=10,
left=60,
blur=ft.Blur(10, 0, ft.BlurTileMode.MIRROR),
width=50,
height=50,
bgcolor="#44CCCCCC",
border=ft.border.all(2, ft.Colors.BLACK),
),
]
)
border: Border | None = None
A border to draw above the background color.
Value is of type Border.
If specified, the corners of the container are rounded by this radius.
Value is of type BorderRadius.
Effective inside Stack only. The distance
that the child's bottom edge is inset from the bottom of the stack.
clip_behavior: ClipBehavior | None = None
The content will be clipped (or not) according to this option.
Value is of type ClipBehavior
and defaults to ClipBehavior.ANTI_ALIAS if border_radius is not None;
otherwise ClipBehavior.NONE.
col: ResponsiveNumber = 12
If a parent of the control is ResponsiveRow, col property is used to determine
how many virtual columns of a screen the control will span.
Can be a number or a dictionary configured to have a different value for specific
breakpoints, for example col={"sm": 6}. Breakpoints are named dimension ranges:
| Breakpoint | Dimension |
|---|---|
| xs | <576px |
| sm | ≥576px |
| md | ≥768px |
| lg | ≥992px |
| xl | ≥1200px |
| xxl | ≥1400px |
If col property is not specified, it spans the maximum number of columns (12).
color_filter: ColorFilter | None = None
Applies a color filter to the container.
Value is of type ColorFilter.
dark_theme: Theme | None = None
Allows setting a nested theme to be used when in dark theme mode for all controls
inside the container and down the tree.
Value is of type Theme.
disabled: bool = False
Every control has disabled property which is False by default - control and all
its children are enabled.
disabled property is mostly used with data entry controls like TextField,
Dropdown, Checkbox, buttons.
However, disabled could be set to a parent control and its value will be
propagated down to all children recursively.
For example, if you have a form with multiple entry controls you can disable them all together by disabling container:
When a child Control is placed into a Column
or a Row you can "expand" it to fill the
available space.
expand property could be a boolean value (True - expand control to fill all
available space) or an integer - an "expand factor" specifying how to divide a free
space with other expanded child controls.
For more information and examples about expand property see "Expanding children"
sections in Column or
Row.
Here is an example of expand being used in action for both Column
and Row:
import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
page.spacing = 0
page.padding = 0
page.add(
ft.Column(
controls=[
ft.Row(
[
ft.Card(
content=ft.Text("Card_1"),
color=ft.Colors.ORANGE_300,
expand=True,
height=page.height,
margin=0,
),
ft.Card(
content=ft.Text("Card_2"),
color=ft.Colors.GREEN_100,
expand=True,
height=page.height,
margin=0,
),
],
expand=True,
spacing=0,
),
],
expand=True,
spacing=0,
),
)
ft.app(main)
expand_loose: bool | None = None
Effective only if expand is True.
If expand_loose is True, the child control of a
Column or a Row
will be given the flexibility to expand to fill the available space in the main
axis (e.g., horizontally for a Row or vertically for a Column), but will not be
required to fill the available space.
The default value is False.
Here is the example of Containers placed in Rows with expand_loose = True:
import flet as ft
class Message(ft.Container):
def __init__(self, author, body):
super().__init__()
self.content = ft.Column(
controls=[
ft.Text(author, weight=ft.FontWeight.BOLD),
ft.Text(body),
],
)
self.border = ft.border.all(1, ft.Colors.BLACK)
self.border_radius = ft.border_radius.all(10)
self.bgcolor = ft.Colors.GREEN_200
self.padding = 10
self.expand = True
self.expand_loose = True
def main(page: ft.Page):
chat = ft.ListView(
padding=10,
spacing=10,
controls=[
ft.Row(
alignment=ft.MainAxisAlignment.START,
controls=[
Message(
author="John",
body="Hi, how are you?",
),
],
),
ft.Row(
alignment=ft.MainAxisAlignment.END,
controls=[
Message(
author="Jake",
body="Hi I am good thanks, how about you?",
),
],
),
ft.Row(
alignment=ft.MainAxisAlignment.START,
controls=[
Message(
author="John",
body="Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and
typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's
standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown
printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a
type specimen book.",
),
],
),
ft.Row(
alignment=ft.MainAxisAlignment.END,
controls=[
Message(
author="Jake",
body="Thank you!",
),
],
),
],
)
page.window.width = 393
page.window.height = 600
page.window.always_on_top = False
page.add(chat)
ft.run(main)

figure: Figure = field(metadata={'skip': True})
Matplotlib figure to draw - an instance of
matplotlib.figure.Figure.
foreground_decoration: BoxDecoration | None = None
The foreground decoration.
Value is of type BoxDecoration.
gradient: Gradient | None = None
Defines the gradient background of the container.
Value is of type Gradient.
ignore_interactions: bool = False
Whether to ignore all interactions with this container and its descendants.
Defaults to False.
image: DecorationImage | None = None
An image to paint above the bgcolor or gradient. If shape=BoxShape.CIRCLE
then this image is clipped to the circle's boundary; if border_radius is not
None then the image is clipped to the given radii.
Value is of type DecorationImage.
ink: bool = False
True to produce ink ripples effect when user clicks the container.
Defaults to False.
Effective inside Stack only. The distance
that the child's left edge is inset from the left of the stack.
Empty space to surround the decoration and child control.
Value is of type Margin class or
a number.
offset: OffsetValue | None = None
Applies a translation transformation before painting the control.
The translation is expressed as a transform.Offset scaled to the control's size.
For example, an Offset with a x of 0.25 will result in a horizontal
translation of one quarter the width of the control.
The following example displays container at 0, 0 top left corner of a stack as
transform applies -1 * 100, -1 * 100 (offset * control_size) horizontal and
vertical translations to the control:
on_animation_end: OptionalControlEventHandler[
ConstrainedControl
] = None
All controls with animate_* properties have on_animation_end event handler
which is called when animation complete and can be used to chain multiple
animations.
Event's object data field contains the name of animation:
opacityrotationscaleoffsetpositioncontainer
For example:
on_click: OptionalControlEventHandler[Container] = None
Fires when a user clicks the container. Will not be fired on long press.
on_hover: OptionalControlEventHandler[Container] = None
Fires when a mouse pointer enters or exists the container area. data property of
event object contains true (string) when cursor enters and false when it exits.
A simple example of a container changing its background color on mouse hover:
on_long_press: OptionalControlEventHandler[Container] = None
Fires when the container is long-pressed.
Fires when a user clicks the container with or without a long press.
Event handler argument is of type TapEvent.
Info
If ink is True, e will be plain ControlEvent with empty data instead of
ContainerTapEvent.
A simple usage example:
import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
page.vertical_alignment = ft.MainAxisAlignment.CENTER
page.horizontal_alignment = ft.CrossAxisAlignment.CENTER
def on_long_press(e):
print("on long press")
page.add(ft.Text("on_long_press triggered"))
def on_click(e):
print("on click")
page.add(ft.Text("on_click triggered"))
def on_tap_down(e: ft.ContainerTapEvent):
print("on tap down", e.local_x, e.local_y)
page.add(ft.Text("on_tap_down triggered"))
c = ft.Container(
bgcolor=ft.Colors.RED,
content=ft.Text("Test Long Press"),
height=100,
width=100,
on_click=on_click,
on_long_press=on_long_press,
on_tap_down=on_tap_down,
)
page.add(c)
ft.app(main)
opacity: Number = 1.0
Defines the transparency of the control.
Value ranges from 0.0 (completely transparent) to 1.0 (completely opaque
without any transparency) and defaults to 1.0.
original_size: bool = False
Whether to display chart in original size.
Set to False to display a chart that fits configured bounds.
Empty space to inscribe inside a container decoration (background, border). The child control is placed inside this padding.
Value is of type Padding or a
number.
The page (of type Page or PageView) to which this control belongs to.
parent: BaseControl | None
The direct ancestor(parent) of this control.
It defaults to None and will only have a value when this control is mounted (added to the page tree).
The Page control (which is the root of the tree) is an exception - it always has parent=None.
Effective inside Stack only. The distance
that the child's right edge is inset from the right of the stack.
rotate: RotateValue | None = None
Transforms control using a rotation around the center.
The value of rotate property could be one of the following types:
number- a rotation in clockwise radians. Full circle360°ismath.pi * 2radians,90°ispi / 2,45°ispi / 4, etc.transform.Rotate- allows to specify rotationangleas well asalignment- the location of rotation center.
For example:
scale: ScaleValue | None = None
Scale control along the 2D plane. Default scale factor is 1.0 - control is not
scaled. 0.5 - the control is twice smaller, 2.0 - the control is twice larger.
Different scale multipliers can be specified for x and y axis, but setting
Control.scale property to an instance of transform.Scale class.
Either scale or scale_x and scale_y could be specified, but not all of them,
for example:
shape: BoxShape | None = None
Sets the shape of the container.
Value is of type BoxShape and
defaults to BoxShape.RECTANGLE.
theme: Theme | None = None
Allows setting a nested theme for all controls inside the container and down the
tree.
Value is of type Theme.
Usage example
import flet as ft
def main(page: ft.Page):
# Yellow page theme with SYSTEM (default) mode
page.theme = ft.Theme(
color_scheme_seed=ft.Colors.YELLOW,
)
page.add(
# Page theme
ft.Container(
content=ft.ElevatedButton("Page theme button"),
bgcolor=ft.Colors.SURFACE_CONTAINER_HIGHEST,
padding=20,
width=300,
),
# Inherited theme with primary color overridden
ft.Container(
theme=ft.Theme(color_scheme=ft.ColorScheme(primary=ft.Colors.PINK)),
content=ft.ElevatedButton("Inherited theme button"),
bgcolor=ft.Colors.SURFACE_CONTAINER_HIGHEST,
padding=20,
width=300,
),
# Unique always DARK theme
ft.Container(
theme=ft.Theme(color_scheme_seed=ft.Colors.INDIGO),
theme_mode=ft.ThemeMode.DARK,
content=ft.ElevatedButton("Unique theme button"),
bgcolor=ft.Colors.SURFACE_CONTAINER_HIGHEST,
padding=20,
width=300,
),
)
ft.app(main)
theme_mode: ThemeMode | None = None
Setting theme_mode "resets" parent theme and creates a new, unique scheme for all
controls inside the container. Otherwise the styles defined in container's theme
property override corresponding styles from the parent, inherited theme.
Value is of type ThemeMode and
defaults to ThemeMode.SYSTEM.
tooltip: TooltipValue | None = None
The tooltip property supports both strings
and Tooltip objects.
Effective inside Stack only. The distance
that the child's top edge is inset from the top of the stack.
url: str | None = None
The URL to open when the container is clicked. If provided, on_click event is
fired after that.
url_target: UrlTarget | None = None
Where to open URL in the web mode.
Value is of type UrlTarget and
defaults to UrlTarget.BLANK.
visible: bool = True
Every control has visible property which is True by default - control is
rendered on the page. Setting visible to False completely prevents control (and
all its children if any) from rendering on a page canvas. Hidden controls cannot be
focused or selected with a keyboard or mouse and they do not emit any events.
Examples#
Example 1#
Based on an official Matplotlib example.
import flet as ft
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import flet_charts as fch
matplotlib.use("svg")
def main(page: ft.Page):
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fruits = ["apple", "blueberry", "cherry", "orange"]
counts = [40, 100, 30, 55]
bar_labels = ["red", "blue", "_red", "orange"]
bar_colors = ["tab:red", "tab:blue", "tab:red", "tab:orange"]
ax.bar(fruits, counts, label=bar_labels, color=bar_colors)
ax.set_ylabel("fruit supply")
ax.set_title("Fruit supply by kind and color")
ax.legend(title="Fruit color")
page.add(fch.MatplotlibChart(figure=fig, expand=True))
ft.run(main)
Example 2#
Based on an official Matplotlib example.
import flet as ft
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import flet_charts as fch
matplotlib.use("svg")
def main(page: ft.Page):
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
dt = 0.01
t = np.arange(0, 30, dt)
nse1 = np.random.randn(len(t)) # white noise 1
nse2 = np.random.randn(len(t)) # white noise 2
# Two signals with a coherent part at 10Hz and a random part
s1 = np.sin(2 * np.pi * 10 * t) + nse1
s2 = np.sin(2 * np.pi * 10 * t) + nse2
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1)
axs[0].plot(t, s1, t, s2)
axs[0].set_xlim(0, 2)
axs[0].set_xlabel("time")
axs[0].set_ylabel("s1 and s2")
axs[0].grid(True)
cxy, f = axs[1].cohere(s1, s2, 256, 1.0 / dt)
axs[1].set_ylabel("coherence")
fig.tight_layout()
page.add(fch.MatplotlibChart(figure=fig, expand=True))
ft.run(main)

